A land appraisal is the process of determining the market value of a piece of land, typically conducted by a certified appraiser. The appraisal considers various factors to estimate the land’s worth, whether for sale, development, taxation, Insurance or financing purposes. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Purpose of the Appraisal
- Buying or Selling: To determine a fair purchase price.
- Loan or Mortgage: To secure financing, where the lender requires the value of the land as collateral.
- Taxation: To establish property tax values.
- Development: To analyze the feasibility of a project on the land.
- Eminent Domain: To assess compensation for land taken by the government.
- Insurance Purposes: To assess the land value compared to one with improvements.
2. Factors Considered
- Location: Proximity to surounding neighborhoods, amenities, freeway access and infrastructure.
- Size and Shape: Larger parcels may have higher values, though irregular shapes can affect usability.
- Zoning and Land Use: Permitted uses (e.g., residential, commercial, agricultural) influence the value.
- Topography and Soil Quality: Flat, well-drained land suitable for construction or farming is often valued higher.
- Utilities and Access: Availability of water, electricity, sewage, and ease of access improve valuation.
- Environmental Conditions: Wetlands, flood zones, or contamination can lower value.
- Comparable Sales (Comps): Recent sales of similar properties in the area provide a market benchmark.
- Market Trends: Economic conditions, supply and demand, and development in the area.
3. Appraisal Process
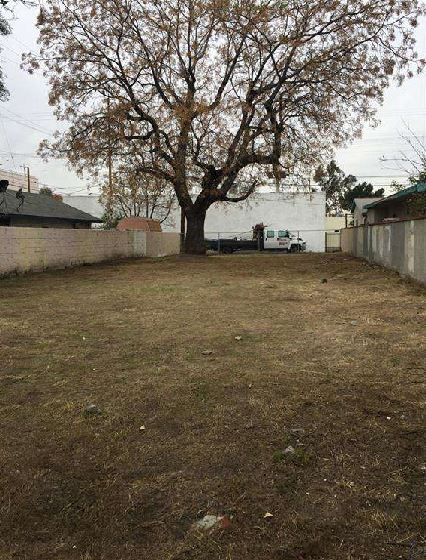

- Inspection: The appraiser visits the site to evaluate its condition and features.
- Research: Analyzing zoning regulations, market trends, and comparable property data.
- Valuation Methods:
- Sales Comparison Approach: Comparing the land to recently sold, similar properties.
- Cost Approach: Estimating the cost of improvements (if applicable) and subtracting depreciation.
- Income Approach: Used if the land generates income (e.g., through leases or interim use).
- Report Preparation: The appraiser compiles findings in a detailed report, outlining the land’s value, reasoning, and supporting data.
4. Deliverables Reports and uses
- Appraisal Report: Includes the final valuation, methodologies used, and a summary of factors influencing the valuation.
- Intended Use: The report specifies the purpose, whether for sale, taxation, insurance negotiations or legal proceedings.
5. Importance of an Accurate Appraisal
- Ensures fair pricing for buyers and sellers.
- Protects clients from over or under valued collateral.
- Assists in planning and budgeting for development projects.
- Prevents disputes in legal or tax matters.
In summary, a land appraisal is a crucial step in understanding the value of a property, enabling informed decisions for various real estate and financial purposes.